What is a stroke?
A stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident or CVA is when part of the brain loses its blood supply and the part of the body that the blood-deprived brain cells control stops working. This loss of blood supply can be ischemic because of lack of blood flow, or hemorrhagic because of bleeding into brain tissue.
There are two types of Stroke:
- Ischemic stroke (part of the brain loses blood flow)
- Transient ischemic attack, TIA, or ministroke (The stroke symptoms resolve within minutes, but may take up to 24 hours on their own without treatment. This is a warning sign that a stroke may occur in the near future.)
- Hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding occurs within the brain)
What are the symptoms of stroke?
Symptoms of stroke depend upon what are of the brain has been affected but may include any of the following:
- Acute change in level of consciousness or confusion
- Severe weakness or paralysis of half or part of the body
- Numbness of one half or part of the body
- Partial vision loss
- Double vision
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Difficulty with balance and vertigo
The symptoms of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke may be the same but hemorrhagic stroke may also cause headache and vomiting.
Are strokes preventable?
People at risk for stroke include those who have high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and those who smoke. People with heart rhythm disturbances, especially atrial fibrillation are also at risk. You can prevent stroke by quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and exercising on a regular basis.
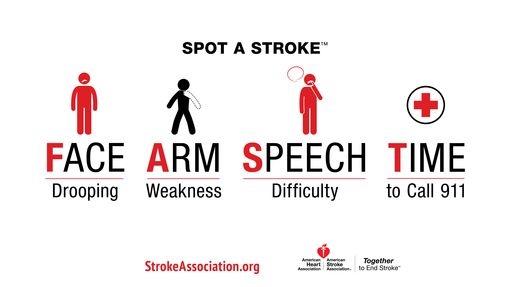
Remember FAST if you think someone might be having a stroke:
- Face drooping
- Arm weakness
- Speech difficulty
- Time to call 9-1-1
A stroke is a medical emergency as strokes can lead to death or permanent disability.
What happens after a stroke?
Emergency treatment for stroke depends on whether the stroke is ischemic or hemorrhagic.
To treat an ischemic stroke, doctors must quickly restore blood flow to your brain. Therapy with clot-busting drugs must start within 4.5 hours in order to be effective. Quick treatment not only improves your chances of survival but also may reduce complications.
Emergency treatment of hemorrhagic stroke focuses on controlling bleeding and reducing pressure in the brain. Surgery may also be needed to lower risk of stroke in the future. Once the brain bleed stops, treatment usually involves supportive medical care while the body absorbs blood. If the area of bleeding is large, surgery may be needed to remove the blood and relieve pressure.